
According to SI system unit of Impulse will be newton second or N.m. Impulse is equivalent to a change in momentum, This can be mathematically written as- F t m v The left-hand side of the equation clearly says that Force is multiplied by time to give impulse. Now, calculate the impulse of the object. The units of impulse can be derived using the Impulse-momentum theorem. This means that every secondthat AddForce is called, the velocity increases by force/mass. If the force of an impulse is changing with time, then the impulse is measured by finding the area bound by the force-time graph for that force. It is given by I F dt The impulse of a force is a vector quantity and its SI unit is 1 Nm.
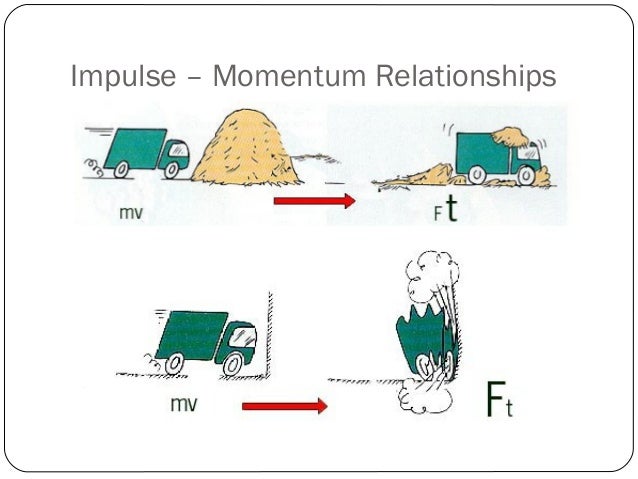
For any system we assume that change in momentum is equal to impulse. Forceis in the units of force: Newtons, or a kgm/(s2). Impulse is defined as the product of force and the small time interval for which it acts. We defined two new physical quantities: momentum (mdelta v) and impulse (Fdelta t). The symbols mean as follows: the mass of the. Moreover, after hitting the wall its velocity becomes -10 m/s (it is negative because it has bounced back in the opposite direction). These are documented with the 3D ForceMode, but the principle is the same in 2D. The impulse of a force, usually denoted by p p or by J J can be defined in two ways according to the following derivation from Newton's Second Law. Furthermore, before hitting the wall, the mass of the object is 2.0 kg and its velocity is 10 m/s. The name unit comes from the integral of the force over time t, which results in the unit change of the linear momentum I: (1. In this example, the object first collides with the wall and then bounce back. (1.76) which is zero for all values of t, except at, as the amplitude goes to infinity. If the wright of the object was 2.0 kg and the object travels with a velocity of 10 m/s before it hit the wall. The units of impulse can be derived using the Impulse-momentum theorem. Solved Example on Impulse Formula Example 1Īn object collides with a solid wall and after the collision, it stops. Also, impulse has two different units, it can either kilogram meter per second (kg m/s) or Newton times seconds (Ns). Most noteworthy, the formula relates impulse to the change in the momentum of the object. \(\vec\) = refers to the initial momentum Besides, a slow-moving large object has large momentum also, a small but fast-moving object has a large momentum.Īs an example, suppose a Bowling ball and Ping-Pong ball have the same velocity, then the Bowling ball will have greater momentum because it is bigger than the Ping-Pong ball.
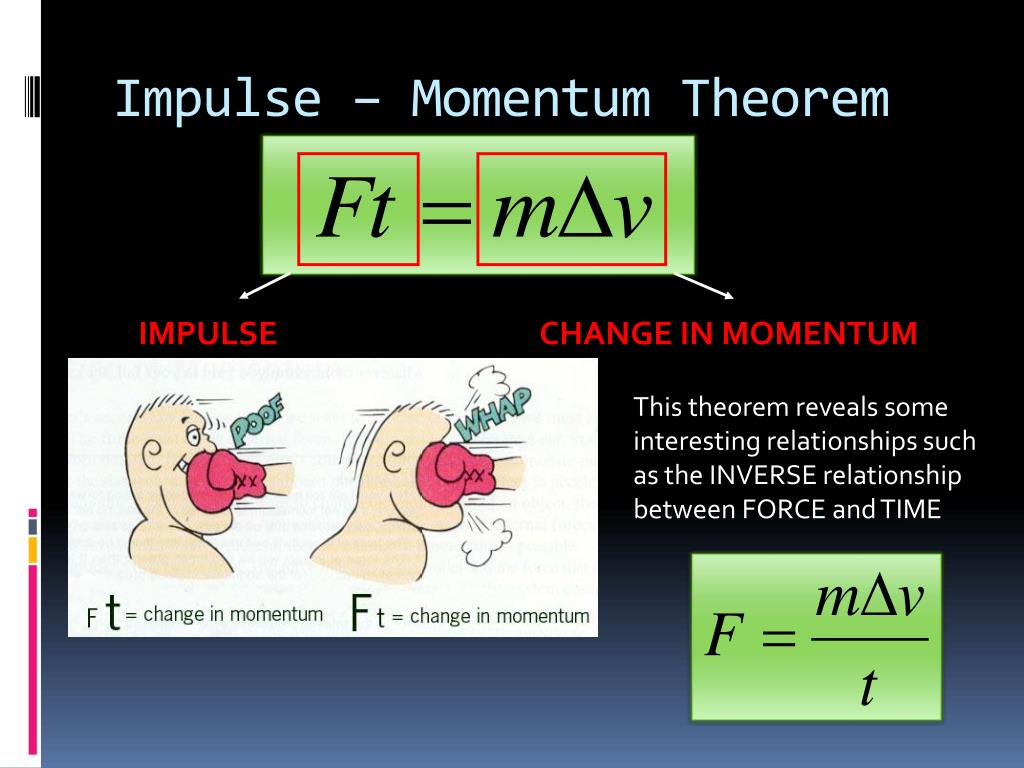
Moreover, an object that is stable or stationary has no or zero momentum. In addition, we can approximate the external force f(t) by using the unit impulse functions (t ) and (t 2) of course, since the impulse in both. Also, it is a measure of how difficult it is to stop an object. Momentum refers to the measure of strength. Hence, the question here is what is impulse and what it has to do with these situations?īefore discussing impulse we first need to converse about the concept of momentum. in all these things we use impulse without knowing it.
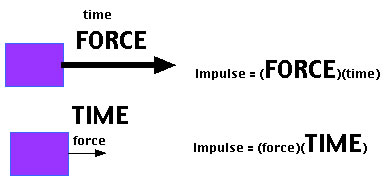
In our daily life, we have kicked a ball, hit a punching bag, and played sports that involve any kind of ball, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
